Motherboards
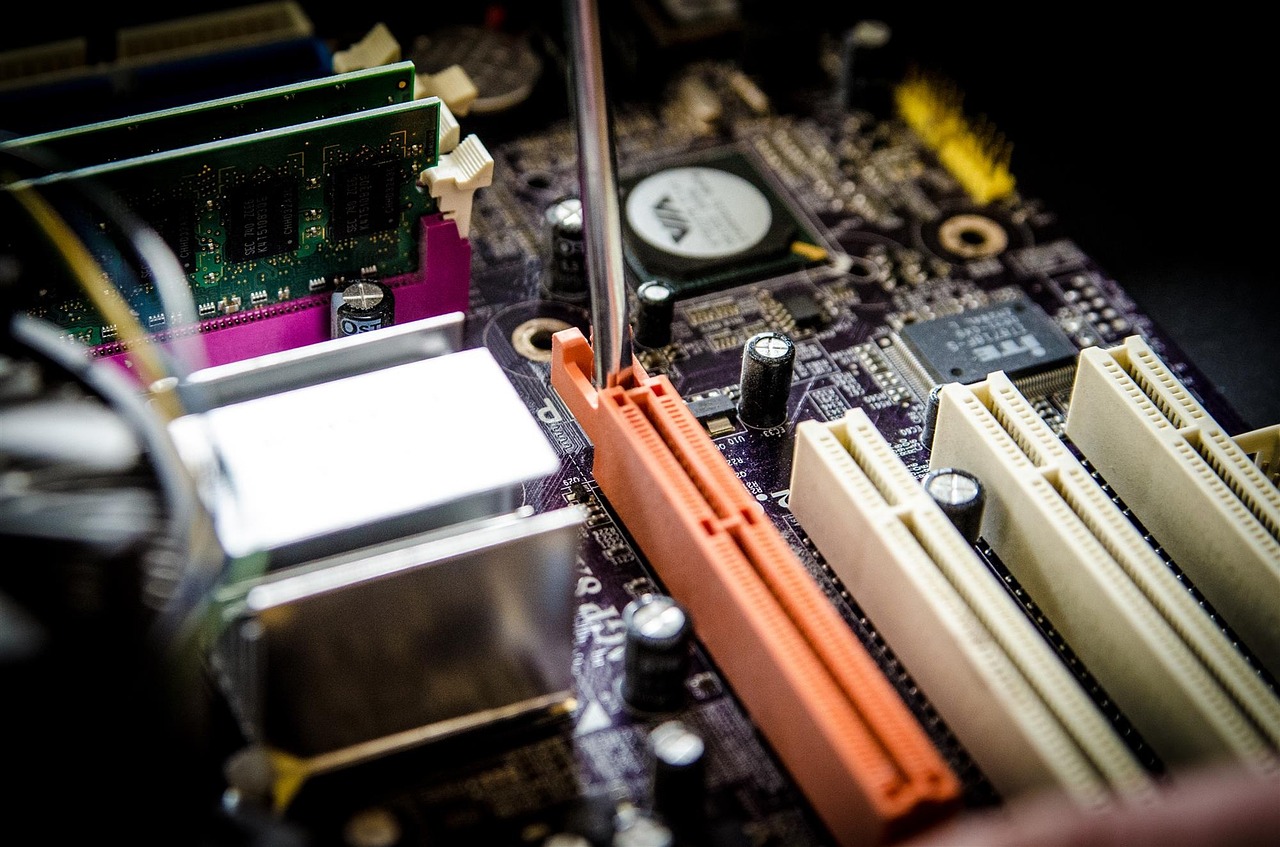
Motherboards are the central hub of any computer system, connecting all the various components and allowing them to communicate with each other. They come in a range of shapes and sizes, from the tiny motherboards found in laptops to the large, full-sized motherboards used in desktop computers. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at motherboards and explore their components, features, and functions.
Components of a Motherboard
Motherboards are made up of several key components, including:
-
CPU Socket: The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer, and it plugs into a socket on the motherboard. Different motherboards are designed to work with different types of CPUs, so it’s important to choose a motherboard that’s compatible with your CPU.
-
Memory Slots: Motherboards have slots for installing memory modules (RAM), which provide temporary storage for the computer’s data. The number and type of memory slots vary depending on the motherboard.
-
Expansion Slots: Motherboards have expansion slots that allow you to add additional components, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards. The most common types of expansion slots are PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect).
-
Power Connector: Motherboards require power to operate, which is supplied through a connector on the motherboard. The most common type of power connector is the 24-pin ATX connector.
-
Chipset: The chipset is responsible for managing the communication between the CPU, memory, and other components. It’s usually located near the CPU socket and is an important factor in determining the motherboard’s performance.
Features of a Motherboard
Motherboards come with a wide range of features, including:
-
Form Factor: The form factor of a motherboard refers to its size and shape. The most common form factors are ATX, micro-ATX, and mini-ITX.
-
USB Ports: Most motherboards have several USB ports, which allow you to connect a range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, and external hard drives.
-
SATA Ports: SATA (Serial ATA) ports are used to connect storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs).
-
Network Interface: Motherboards typically have a network interface, which allows you to connect to a wired or wireless network.
-
Audio and Video Ports: Motherboards usually have audio and video ports, which allow you to connect speakers, headphones, and monitors.
Functions of a Motherboard
The primary function of a motherboard is to provide a platform for all the components in a computer system to communicate with each other. It does this by providing a system bus, which is a set of wires that connect the CPU, memory, and other components. The motherboard also provides power to the components, and it manages the flow of data between them.
In addition to these basic functions, motherboards can also provide a range of advanced features, such as overclocking capabilities, built-in Wi-Fi, and support for multiple graphics cards.
Conclusion
Motherboards are a critical component of any computer system, providing the foundation for all the other components to function. By understanding the components, features, and functions of motherboards, you can make informed decisions when building or upgrading your computer system. Whether you’re a hardware enthusiast or a casual user, the motherboard is a crucial piece of technology that you can’t afford to overlook.

Comments